Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the month"
From CannaQAWiki
Jump to navigationJump to searchShawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated article of the month text) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Chambers JofCannRes23 5.png|220px]]</div> | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig1 Chambers JofCannRes23 5.png|220px]]</div> | ||
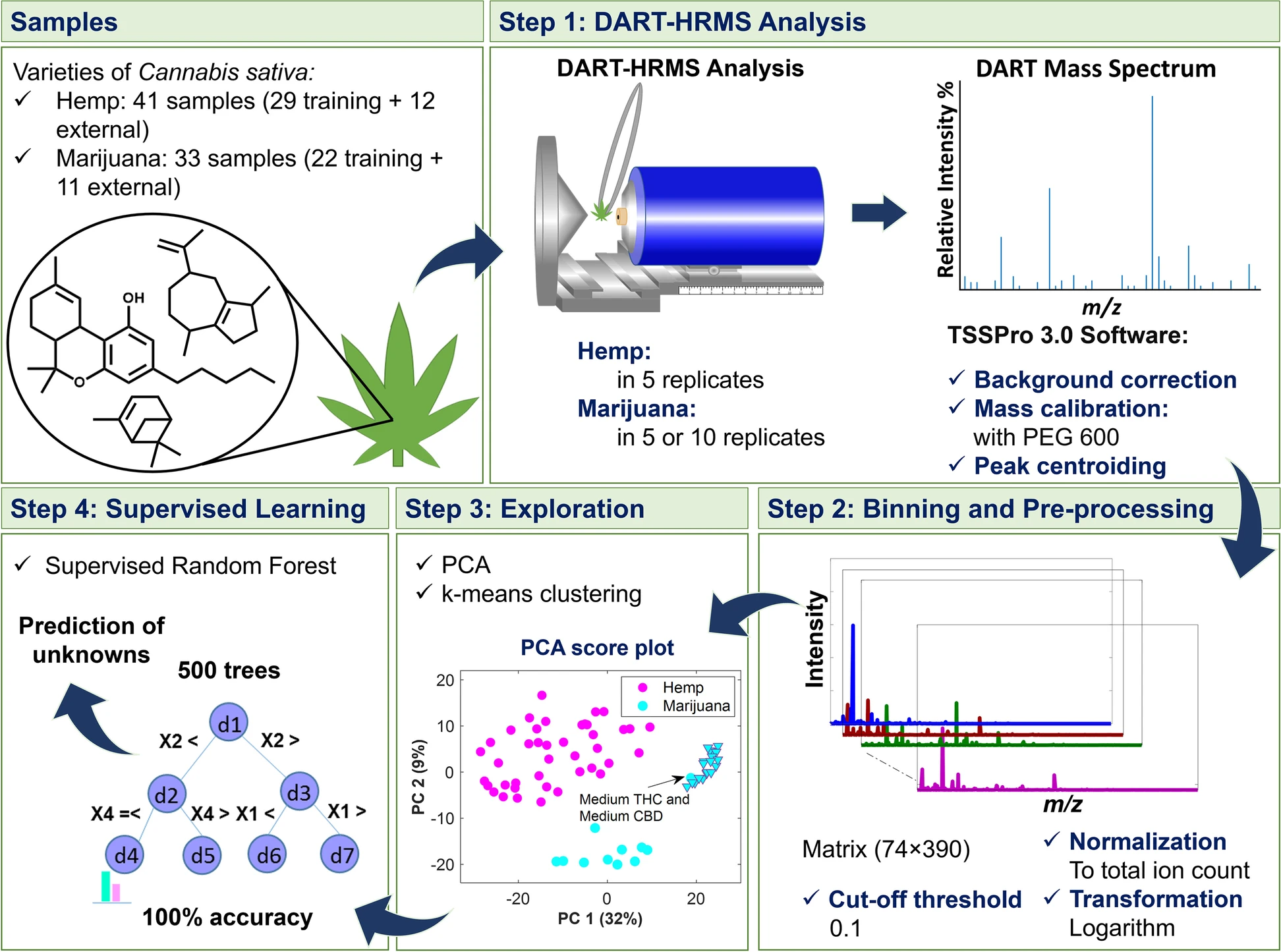
'''"[[Journal:Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of Cannabis sativa|Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of Cannabis sativa]]"''' | '''"[[Journal:Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of Cannabis sativa|Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of ''Cannabis sativa'']]"''' | ||
[[Hemp]] and marijuana are the two major varieties of ''[[Cannabis sativa]]''. While both contain [[Tetrahydrocannabinol|Δ<sup>9</sup>-tetrahydrocannabinol]] (THC), the primary [[Psychoactive drug|psychoactive]] component of ''C. sativa'', they differ in the amount of THC that they contain. Presently, U.S. federal laws stipulate that ''C. sativa'' containing greater than 0.3% THC is classified as marijuana, while plant material that contains less than or equal to 0.3% THC is hemp. Current methods to determine THC content are [[chromatography]]-based, which requires extensive [[Sample (material)|sample]] preparation to render the materials into [[Cannabis concentrate|extracts]] suitable for sample injection, for complete separation and differentiation of THC from all other analytes present ... ('''[[Journal:Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of Cannabis sativa|Full article...]]''')<br /> | [[Hemp]] and marijuana are the two major varieties of ''[[Cannabis sativa]]''. While both contain [[Tetrahydrocannabinol|Δ<sup>9</sup>-tetrahydrocannabinol]] (THC), the primary [[Psychoactive drug|psychoactive]] component of ''C. sativa'', they differ in the amount of THC that they contain. Presently, U.S. federal laws stipulate that ''C. sativa'' containing greater than 0.3% THC is classified as marijuana, while plant material that contains less than or equal to 0.3% THC is hemp. Current methods to determine THC content are [[chromatography]]-based, which requires extensive [[Sample (material)|sample]] preparation to render the materials into [[Cannabis concentrate|extracts]] suitable for sample injection, for complete separation and differentiation of THC from all other analytes present ... ('''[[Journal:Combined ambient ionization mass spectrometric and chemometric approach for the differentiation of hemp and marijuana varieties of Cannabis sativa|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
Revision as of 15:41, 30 June 2023
Hemp and marijuana are the two major varieties of Cannabis sativa. While both contain Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive component of C. sativa, they differ in the amount of THC that they contain. Presently, U.S. federal laws stipulate that C. sativa containing greater than 0.3% THC is classified as marijuana, while plant material that contains less than or equal to 0.3% THC is hemp. Current methods to determine THC content are chromatography-based, which requires extensive sample preparation to render the materials into extracts suitable for sample injection, for complete separation and differentiation of THC from all other analytes present ... (Full article...)
Recently featured:
- ▪ Academic-industry partnership advancing cannabis science: The Complementary Care Practice-Based Research Network
- ▪ Beyond cannabinoids: Application of NMR-based metabolomics for the assessment of Cannabis sativa L. crop health
- ▪ High-throughput methods to identify male Cannabis sativa using various genotyping methods