Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the month"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Created as needed) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated for October) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig3 Krill Metabolites2020 10-7.png|240px]]</div> | ||
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:A high-throughput method for the comprehensive analysis of terpenes and terpenoids in medicinal cannabis biomass|A high-throughput method for the comprehensive analysis of terpenes and terpenoids in medicinal cannabis biomass]]"''' | ||
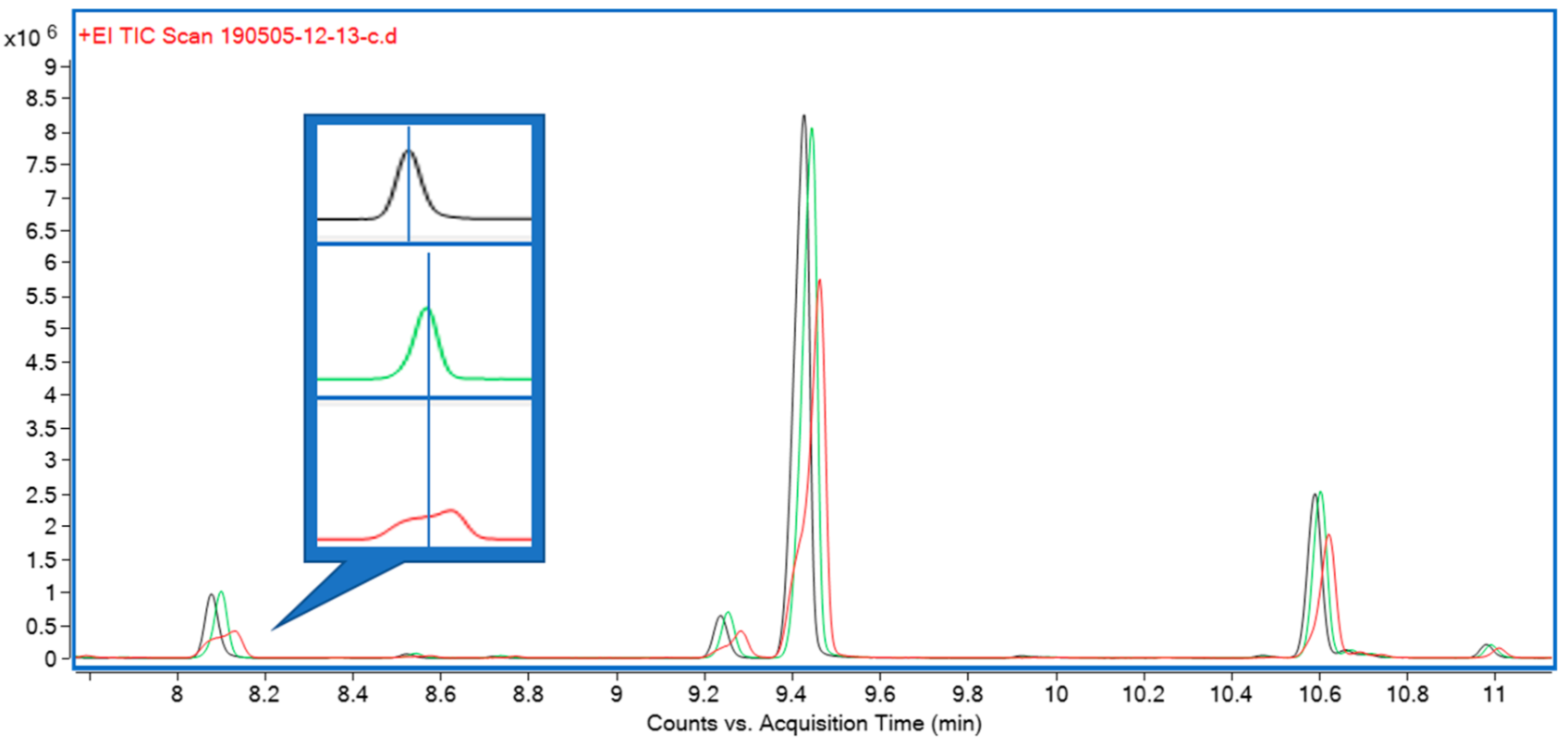
[[Cannabis]] and its secondary metabolite content have recently seen a surge in research interest. Cannabis [[terpene]]s and [[terpenoid]]s in particular are increasingly the focus of research efforts due to the possibility of their contribution to the overall therapeutic effect of [[Cannabis (drug)|medicinal cannabis]]. Current methodology to quantify terpenes in cannabis biomass mostly relies on large quantities of biomass, long extraction protocols, and long [[gas chromatography]] (GC) gradient times, often exceeding 60 minutes. They are therefore not easily applicable in the high-throughput environment of a cannabis breeding program. The method presented here, however, is based on a simple [[wikipedia:Hexane|hexane]] extract from 40 mg of biomass, with 50 μg/mL [[wikipedia:Dodecane|dodecane]] as internal standard, and a gradient of less than 30 minutes. ('''[[Journal:A high-throughput method for the comprehensive analysis of terpenes and terpenoids in medicinal cannabis biomass|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal: | : ▪ [[Journal:Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis|Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis]] | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 6 October 2020
Cannabis and its secondary metabolite content have recently seen a surge in research interest. Cannabis terpenes and terpenoids in particular are increasingly the focus of research efforts due to the possibility of their contribution to the overall therapeutic effect of medicinal cannabis. Current methodology to quantify terpenes in cannabis biomass mostly relies on large quantities of biomass, long extraction protocols, and long gas chromatography (GC) gradient times, often exceeding 60 minutes. They are therefore not easily applicable in the high-throughput environment of a cannabis breeding program. The method presented here, however, is based on a simple hexane extract from 40 mg of biomass, with 50 μg/mL dodecane as internal standard, and a gradient of less than 30 minutes. (Full article...)
Recently featured: