Difference between revisions of "Template:Article of the month"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated for October) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated for November) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File: | <div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Tab1 Montoya FrontPharm2020 11.jpg|240px]]</div> | ||
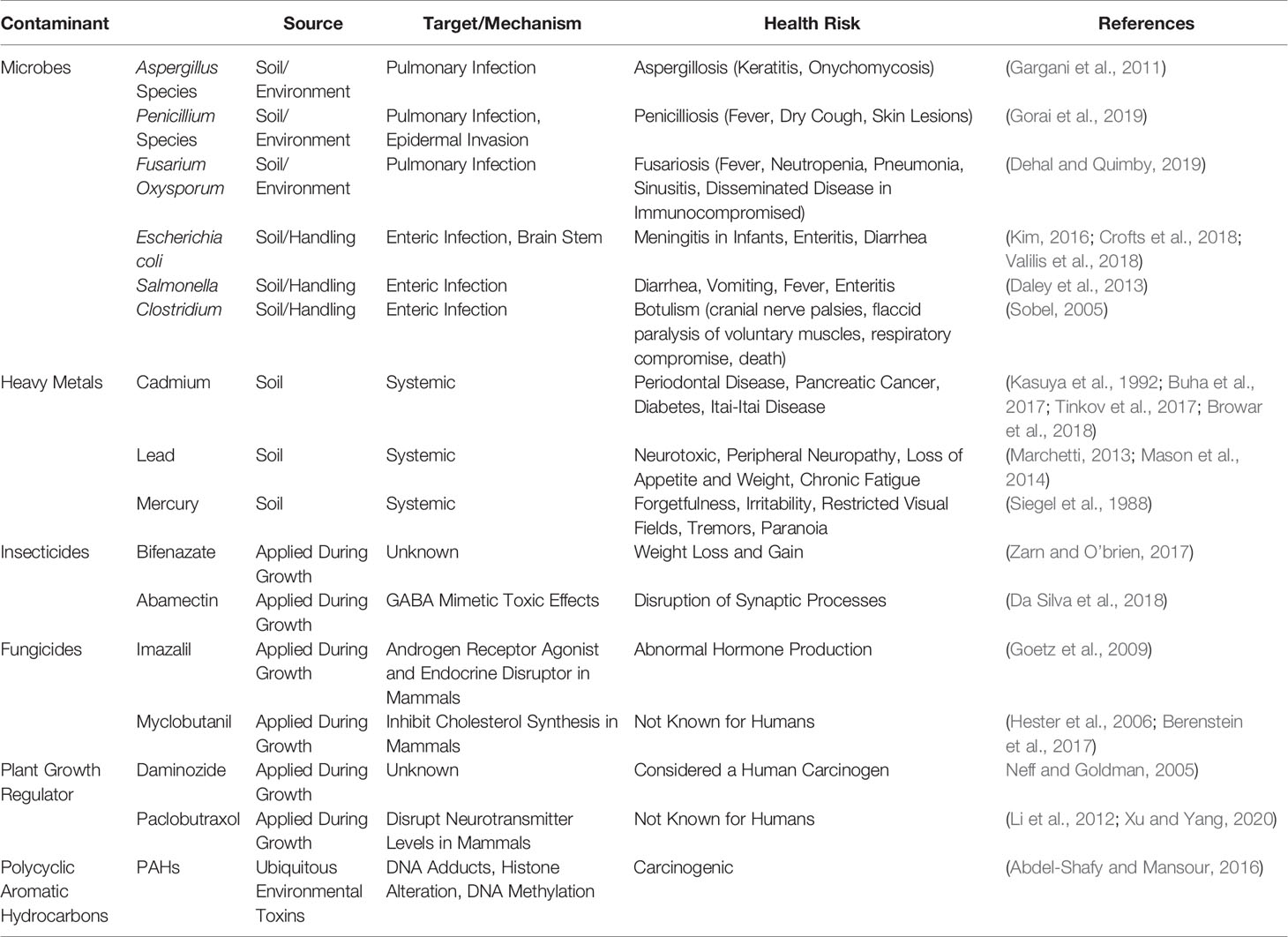
'''"[[Journal: | '''"[[Journal:Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol|Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol]]"''' | ||
[[Cannabis]] and | For nearly a century, [[Cannabis|cannabis]] has been stigmatized and [[Legality of cannabis|criminalized]] across the globe, but in recent years, there has been a growing interest in cannabis due to the therapeutic potential of [[Cannabinoid#Phytocannabinoids|phytocannabinoids]]. With this emerging interest in cannabis, concerns have arisen about the possible [[contamination]]s of [[hemp]] with [[pesticide]]s, [[heavy metals]], [[Microorganism|microbial]] pathogens, and [[wikipedia:Carcinogen|carcinogenic]] compounds during the [[Cannabis cultivation|cultivation]], manufacturing, and packaging processes. This is of particular concern for those turning to cannabis for [[Cannabis (drug)|medicinal purposes]], especially those with compromised immune systems. This review aims to provide types of contaminants and examples of cannabis contamination using case studies that elucidate the medical consequences consumers risk when using adulterated cannabis products. ('''[[Journal:Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol|Full article...]]''')<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
''Recently featured'': | ''Recently featured'': | ||
: ▪ [[Journal:A high-throughput method for the comprehensive analysis of terpenes and terpenoids in medicinal cannabis biomass|A high-throughput method for the comprehensive analysis of terpenes and terpenoids in medicinal cannabis biomass]] | |||
: ▪ [[Journal:Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis|Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis]] | : ▪ [[Journal:Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis|Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis]] | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 4 November 2020
"Cannabis contaminants limit pharmacological use of cannabidiol"
For nearly a century, cannabis has been stigmatized and criminalized across the globe, but in recent years, there has been a growing interest in cannabis due to the therapeutic potential of phytocannabinoids. With this emerging interest in cannabis, concerns have arisen about the possible contaminations of hemp with pesticides, heavy metals, microbial pathogens, and carcinogenic compounds during the cultivation, manufacturing, and packaging processes. This is of particular concern for those turning to cannabis for medicinal purposes, especially those with compromised immune systems. This review aims to provide types of contaminants and examples of cannabis contamination using case studies that elucidate the medical consequences consumers risk when using adulterated cannabis products. (Full article...)
Recently featured: