Difference between revisions of "Main Page/Featured article of the month/2020"
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Created as needed) |
Shawndouglas (talk | contribs) (Updated for October) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | <!-- Below this line begin pasting previous news --> | ||
<h2 style="font-size:105%; font-weight:bold; text-align:left; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em; width:50%;">Featured article of the month: September:</h2> | |||
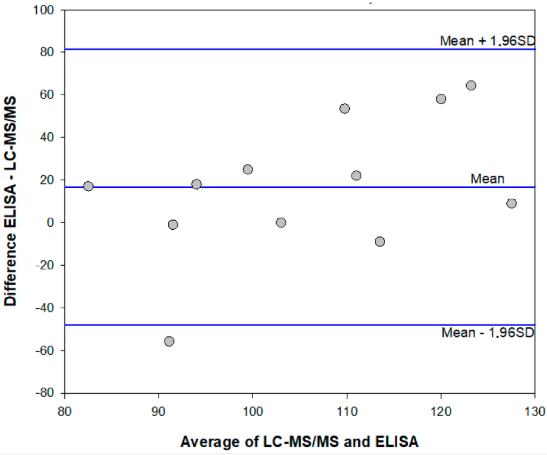
<div style="float: left; margin: 0.5em 0.9em 0.4em 0em;">[[File:Fig2 DiNardo Toxins2020 12-4.png|240px]]</div> | |||
'''"[[Journal:Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis|Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis]]"''' | |||
The diffusion of the legalization of [[cannabis]] for recreational, medicinal, and nutraceutical uses requires the development of adequate analytical methods to assure the safety and security of such products. In particular, [[aflatoxin]]s are considered to pose a major risk for the health of cannabis consumers. Among analytical methods that allow for adequate monitoring of food safety, [[wikipedia:Immunoassay|immunoassay]]s play a major role thanks to their cost-effectiveness, high-throughput capacity, simplicity, and limited requirement for equipment and skilled operators. Therefore, a rapid and sensitive [[wikipedia:Enzyme immunoassay|enzyme immunoassay]] has been adapted to measure the most hazardous [[wikipedia:Aflatoxin B1|aflatoxin B<sub>1</sub>]] in cannabis products. ('''[[Journal:Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis|Full article...]]''')<br /> | |||
|- | |- | ||
|<br /> | |<br /> | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 17:51, 6 October 2020
Featured article of the month archive - 2020
Welcome to the CannaQAwiki 2020 archive for the Featured Article of the Month.
Featured article of the month: September:"Enzyme immunoassay for measuring aflatoxin B1 in legal cannabis" The diffusion of the legalization of cannabis for recreational, medicinal, and nutraceutical uses requires the development of adequate analytical methods to assure the safety and security of such products. In particular, aflatoxins are considered to pose a major risk for the health of cannabis consumers. Among analytical methods that allow for adequate monitoring of food safety, immunoassays play a major role thanks to their cost-effectiveness, high-throughput capacity, simplicity, and limited requirement for equipment and skilled operators. Therefore, a rapid and sensitive enzyme immunoassay has been adapted to measure the most hazardous aflatoxin B1 in cannabis products. (Full article...) |