Journal:Beyond cannabinoids: Application of NMR-based metabolomics for the assessment of Cannabis sativa L. crop health
| Full article title | Beyond cannabinoids: Application of NMR-based metabolomics for the assessment of Cannabis sativa L. crop health |
|---|---|
| Journal | Frontiers in Plant Science |
| Author(s) | Fernández, Santiago; Castro, Rossina; López-Radcenco, Andrés; Rodriguez, Paula; Carrera, Inés; García-Carnelli, Carlos; Moyna, Guillermo |
| Author affiliation(s) | Universidad de la República - Montevideo, Universidad de la República - Paysandú |
| Primary contact | Email: carlosga at fq dot edu dot uy |
| Editors | Firoentino, Nunzio |
| Year published | 2023 |
| Volume and issue | 14 |
| Article # | 1025932 |
| DOI | 10.3389/fpls.2023.1025932 |
| ISSN | 1664-462X |
| Distribution license | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International |
| Website | https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2023.1025932/full |
| Download | https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2023.1025932/pdf (PDF) |
|
|
This article should be considered a work in progress and incomplete. Consider this article incomplete until this notice is removed. |
Abstract
While Cannabis sativa L. varieties have been traditionally characterized by their major cannabinoid profile, it is now well established that other plant metabolites can also have physiological effects, including minor cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. Given the multiple applications of Cannabis in the medical field, it is therefore critical to characterize it according to its chemical composition (i.e., its metabolome) and not only its botanical traits. With this in mind, the cannabinoid and metabolomic profiles from inflorescences of two C. sativa varieties with either high Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) or high cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) contents harvested at different times were studied. According to results from high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and nuclear magnetic resonance-based (NMR-based) untargeted metabolomic analyses of organic and aqueous plant material extracts, we show that in addition to expected variations according to cannabinoid profiles, it is possible to distinguish between harvests of the same variety. In particular, it was possible to correlate variations in the metabolome with presence of powdery mildew, leading to the identification of molecular markers associated with this fungal infection in C. sativa.
Introduction
Cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) is a widely distributed plant that has been a source of fiber, food, oil, and medicines for millennia. [Clarke and Merlin, 2016] The first reports regarding its medicinal use date back to the third millennium BC in ancient China. [Wills, 1998] Since then, several cultures have employed Cannabis preparations to treat a variety of ailments. [Russo, 2014] Since our understanding of its therapeutic potential is continuously improving, the interest in Cannabis as a source of compounds for use in medicinal preparations has increased notably. [Procaccia et al., 2022] Furthermore, the non-pharmacological uses of the plant and its derivatives, particularly as a source of fibers and as a recreational drug, are well known.
C. sativa produces an important number of secondary metabolites, and more than 500 compounds have been identified in Cannabis so far. [ElSohly and Gul, 2014] In particular, cannabinoids, terpenoids, and flavonoids stand out. [ElSohly and Slade, 2005] Of the three compound classes, cannabinoids are of great relevance given their biological activity and the fact that they are almost exclusively found in this plant. [Hanuš et al., 2016; Gülck and Møller, 2020] Most of the known pharmacological properties are associated to these naturally-occurring compounds, particularly Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). These compounds are present mostly as carboxylic acids in the plant—namely Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) and cannabidiolic acid (CBDA)—and are transformed to the neutral molecules through non-enzymatic decarboxylation. [Flores-Sanchez and Verpoorte, 2008]
However, the biological effects of C. sativa do not depend only on the levels of THC and CBD. [Procaccia et al., 2022] Indeed, nearly 150 phytocannabinoids which can be classified in different structural subclasses have been isolated from this plant [Hanuš et al., 2016], and several of these compounds, sometimes referred to as minor cannabinoids, have pharmacological potential. [Franco et al., 2020] Furthermore, a number of studies suggest that the interaction or synergy between these cannabinoids and other secondary metabolites leads to more pronounced effects than those produced by the isolated compounds. [Russo, 2011; Blasco-Benito et al., 2018; Russo, 2019; Maayah et al., 2020; Goerl et al., 2021] In addition, the botanical diversity of C. sativa has resulted in longstanding discussions regarding its taxonomical characterization. It is now generally accepted that the plant is a single species that can be classified in different subspecies and varieties. [Small, 2015; McPartland, 2018] Independent of the names and botanical traits used to refer to it, the chemical composition is what will determine the pharmacological usefulness of the plant. Therefore, several authors stress that the categorization of C. sativa varieties should be done according to its chemical profile [Russo, 2019] and refer to them as chemical varieties or chemovars. [Lewis et al., 2018]
In addition to secondary metabolite content, the quality of a medicinal plant is also given by the absence of contaminants and adulterants. Natural contaminants are usually introduced during cultivation and storage, and they consist of degradation products, microbial contamination, and heavy metals. [American Herbal Pharmacopoeia, 2014] In particular, fungi can colonize different organs of the plant, causing a reduction in the quality of products created from the infected plant. [Punja et al., 2019] Furthermore, the consumption of a contaminated product can cause harmful effects on the health of consumers. [Montoya et al., 2020] Microbial infections can also lead to biotic stress, which can alter the secondary metabolite composition. [Gorelick and Bernstein, 2017]
While the determination of the main cannabinoid content is a required assay for cannabis products that rely on the biological activity of the plant extract, comprehensive knowledge of the profile of other secondary metabolites in these materials is also relevant. [Jin et al., 2021] Thus, establishing the metabolic fingerprints can provide important information to assure the composition and quality of a given C. sativa chemovar. [Puri et al., 2021] Variations in this profile can indicate that the material is not appropriate for its intended uses. In particular, the discrimination between chemovars can be conveniently carried out through nuclear magnetic resonance-based (NMR-based) metabolomic analysis. [Choi et al., 2004a] Indeed, a recent review concludes that metabolomics represents an ideal bioanalytical tool that could greatly assist and accelerate cannabis research and development, even coining the term “cannabinomics.” [Aliferis and Bernard-Perron, 2020]
In the present report we carry out an exhaustive characterization of high-THCA and high-CBDA C. sativa chemovars, both with medicinal potential, through the determination of metabolite profiles complemented with basic information derived from cannabinoid composition. Briefly, our results not only allowed us to clearly distinguish between the two plant varieties, but also to identify a crop with a microbial infection that, interestingly, does not alter the main cannabinoid profile and yield in a relevant way. Furthermore, through metabolomic analysis it was possible to identify variations in specific metabolites that could shed light on infection mechanisms.
Materials and methods
Chemicals and reagents
Analytical grade chloroform and methanol were from Dorwil (Buenos Aires, Argentina), high-performance liquid chromatography-grade (HPLC-grade) acetonitrile was obtained from Carlo Erba (Val-de-Reuil, France), and formic acid, choline (> 98%), deuterochloroform (CDCl3, 99.8%), and deuterium oxide (D2O, 99.9%) were purchased from Merck (Kenilworth, NJ, USA). Betaine (> 98%) was from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Geel, Belgium). Diazepam (> 99.9%) and standard solutions of CBDA, CBD, cannabichromene (CBC), cannabinol (CBN), cannabigerol (CBG), THCA, THC, and Δ8-THC at 1 mg/mL were purchased from Lipomed (Cambridge, MA, USA). Standard solutions of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid (THCVA), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA), cannabidivarin (CBDV) and cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) at 1 mg/mL were purchased from Cerilliant (Round Rock, TX, USA).
Plant material and sample preparation
Cannabis sativa L. female inflorescences were donated by Khiron Life Sciences Uruguay S.A. and employed in compliance with guidelines from a scientific research license granted by the Instituto de Regulación y Control del Cannabis (IRCCA). Plant material from a drug chemotype high in THCA (chemovar A) and a fiber chemotype high in CBDA (chemovar B) were used. Plants were grown under identical indoor conditions, which consisted of temperature and relative humidity ranges of 24-28 °C and 60-70% for the vegetative stage, and 20-26 °C and 55-70% for the flowering stage. Samples were obtained from three different harvests for each chemovar. In the case of chemovar A, these were carried out in March, June, and September 2020, while those for chemovar B harvests were conducted in March, June, and December 2020.
Samples for cannabinoid composition determinations were dried at 35 °C for 24 hours and ground with a manual herb grinder. Once a particle size range from 0.5 to 2 mm was obtained, 500 mg were extracted with a 9:1 methanol-chloroform mixture by dynamic maceration for 30 minutes at room temperature, followed by sonication for 15 minutes. The extract was then filtered and diluted with methanol to a final volume of 50 mL. A 100 μL aliquot of this solution was evaporated under a nitrogen stream and redissolved in 100 μL to 1 mL of acetonitrile containing diazepam (10 μg/mL) as an internal standard. The resulting solutions were employed in chromatographic analyses using the conditions detailed below. These extractions were performed in duplicate.
For NMR-based metabolomic analyses, 20 samples per chemotype from each harvest were collected, frozen in liquid nitrogen, ground manually using a glass rod, and stored at -20 °C. Extractions were carried out following a method originally proposed by Choi et al. [Choi et al., 2004a] Briefly, 500 mg of each sample were suspended in 10 mL of a 1:1:2 methanol-water-chloroform mixture, subjected to vortex agitation for 30 seconds, sonicated for one minute, and then centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 20 minutes. Phases were separated and the extraction of the plant material was repeated. Following phase separation, organic solvents were removed in a rotary evaporator under vacuum at 35 °C, while aqueous phases were dried by lyophilization. Two dry extracts per sample were obtained.
HPLC analysis
The main cannabinoid composition was determined using a recently reported method [Fernández et al., 2022], using a Shimadzu DGU-205R Ultra HPLC-PDA system equipped with a Hypersil C18 (150 × 4.6 mm, 3 μm particle size) column and a Hypersil BDS C18 (10 × 4 mm, 3 μm particle size) precolumn (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Linear calibration curves (r2 > 0.99) for all cannabinoids analyzed were constructed in the range of 1 to 100 μg/mL. The column oven was set to 25 °C, the injection volume was 10 μL, and the total run time was 18 minutes using a solvent gradient composed of 1.0 mM formic acid buffer at pH 3.53 (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) as mobile phase at 1 mL/min flow. The gradient started with 70% B for seven minutes, then increased to 83.5% B and held constant for one minute, then increased to 88.5% B over a three-minute period, one additional minute to reach 99% B, then kept constant for two minutes followed by two minute to lower B to 70%, and finally held constant for two minutes. This method allowed the separation of the 14 cannabinoids available from a mix of standards.
NMR experiments
Organic extracts were dissolved in 0.7 mL of CDCl3 and aqueous extracts in 0.7 mL of D2O, and then transferred to 5 mm NMR tubes (New Era Enterprises Inc., Vineland, NJ, USA). All NMR spectra were recorded at 25 °C on a Bruker AVANCE III 500 NMR spectrometer operating at 1H and 13C frequencies of 500.13 and 125.76 MHz, respectively, and equipped with a z-gradient TXI probe. A spectral width of 10 KHz, a data size of 32 K, and a total of 64 scans were employed to record 1D spectra, using a relaxation delay of four seconds between scans. Regular 1D acquisition sequences with 30° excitation pulses were employed, using a standard water presaturation scheme with aqueous samples. When required, 1D-TOCSY, 1D-NOESY, HSQC, and HMBC spectra were acquired and processed using acquisition and processing parameters provided with the spectrometer.
To confirm the presence of choline and betaine in the aqueous extracts, 10 μL aliquots from 50 mM standard solutions of each compound were added to selected samples, and the 1D 1H NMR experiments repeated under the same conditions described above.
NMR data processing
NMR data for metabolomic analyses were processed and analyzed with MNova (version 12.0, MestreLab Research, S.L., Santiago de Compostela, Spain). Free induction decays were zero-filled to 64 K points and apodized with a 0.3 Hz exponential window function prior to Fourier transformation. All spectra were manually phase- and baseline-corrected and referenced. In the case of organic extracts, the residual CHCl3 solvent signal at 7.28 ppm was used for calibration, while the anomeric proton signal of α-glucose at 5.22 ppm was employed in aqueous samples. Spectra corresponding to the same class of extract were aligned using PAFFT [Wong et al., 2005], and the data was normalized to the total spectral area after excluding residual solvent resonances and regions without signals. The resulting data matrices were finally exported as text files for use in statistical analyses.
Multivariate statistical analysis
Multivariate statistical analyses, including principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), were carried out with the PLS_Toolbox package (version 8.5, Eigenvector Research Inc., Manson, WA, USA) implemented for MATLAB (revision 2014a, The MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA). For all models, the data was mean-centered and scaled using a Pareto factor. [van den Berg et al., 2006] Analysis of the data was first performed with PCA, which reduces the dimensionality and facilitates the identification of data clusters or trends. [Wold et al., 1987; Trygg and Wold, 2002; Trygg et al., 2007] The PCA scores plot was also employed to identify strong outliers outside the 95% significance region of Hotelling’s T2 ellipse. Cross-validation of OPLS-DA models was achieved using the random subset method, which involved 20 iterations over data split into 10 equally-sized parts. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted, and areas under the curves were calculated to ensure the goodness of fit of the resulting models. [Ekelund, 2012; Simundic, 2012] Permutation tests with 100 iterations were also performed to determine the degree of over-fitting and further validate the discriminant analyses. [Ni et al., 2008] When needed, statistical total correlation spectroscopy (STOCSY) analyses were performed with an in-house MATLAB script based on the algorithm described by Cloarec and coworkers. [Cloarec et al., 2005]
Fungi characterization
The fungal infection was evidenced by the presence of off-white powdery spots typical of powdery mildew disease. Microscopic examination of fungi was carried out with a Nikon Eclipse E100 optical microscope. To examine asexual morphs, a piece of clear adhesive tape was placed on infected leaves, stripped off, and placed on a microscope slide with one drop of distilled water. The observations were done at magnifications of 40, 100, and 400 under standard light. Germinated conidia were examined on fungi grown with potato dextrose agar medium.
Results
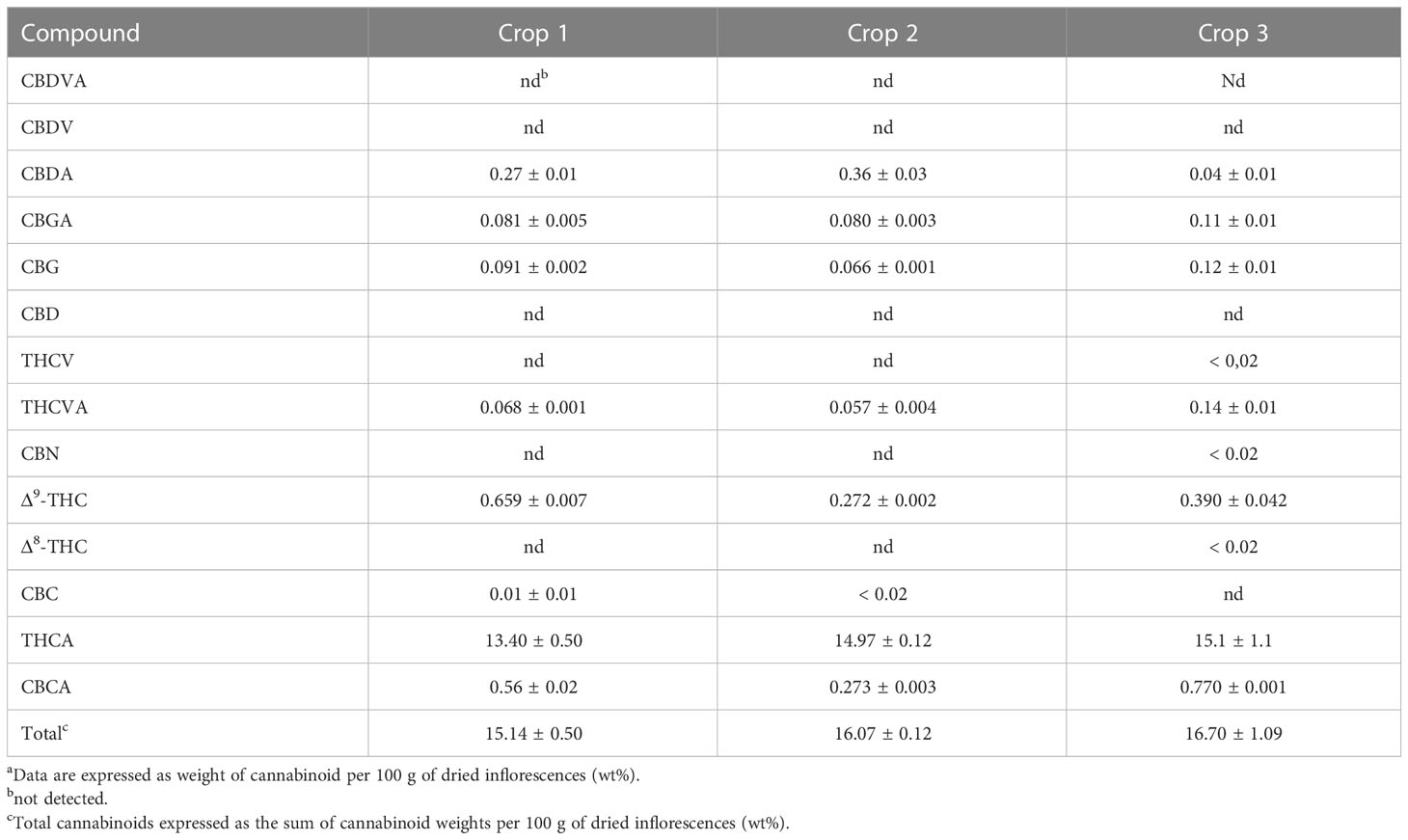
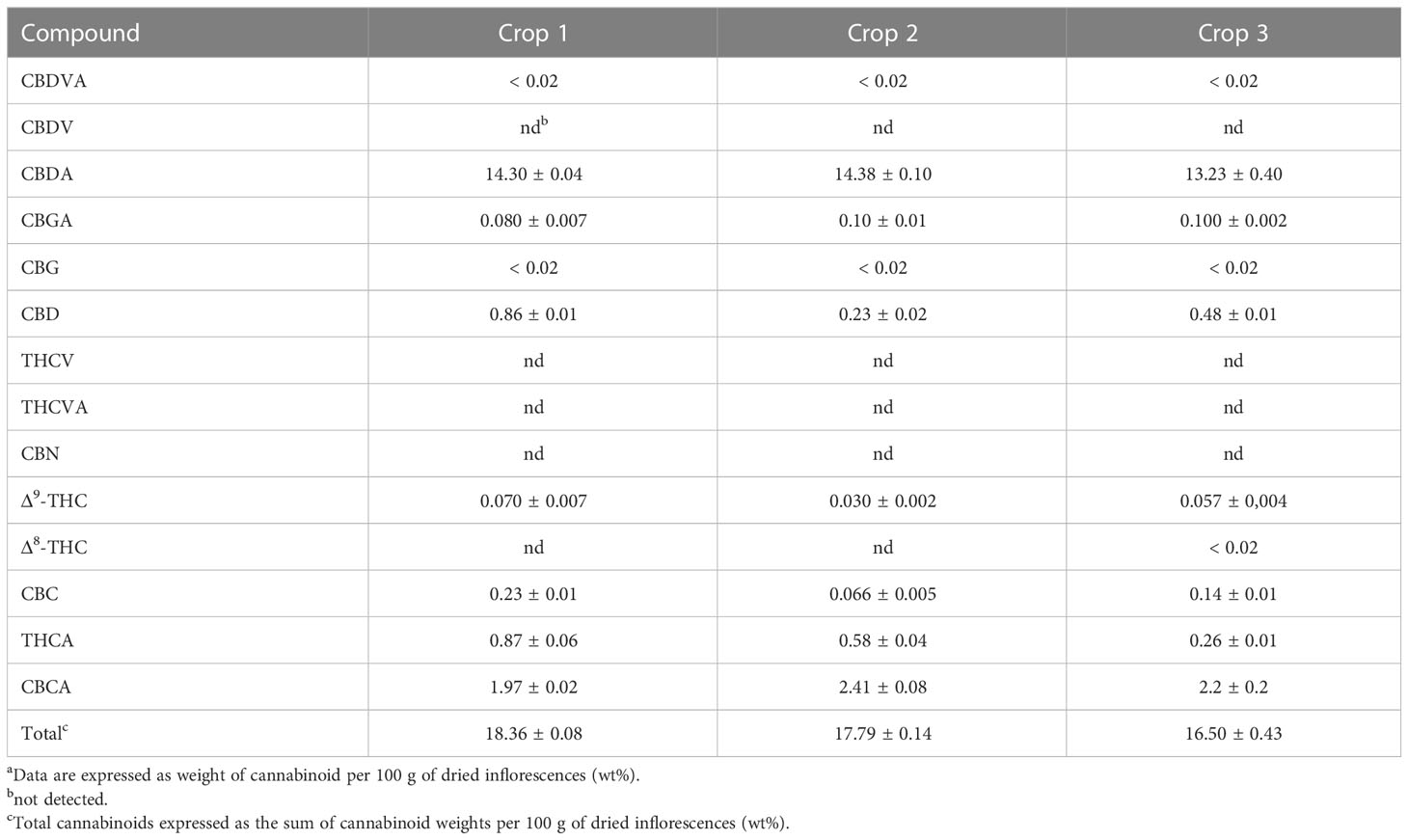
Tables 1 and 2 show the cannabinoid composition of chemovars A and B, respectively. As expected, the two are notably different, and characterized, respectively, by their particularly high content of THCA and CBDA. Moreover, the acidic forms of other cannabinoids are also predominant, and CBN was only detected in one sample and below the quantification limits. This suggests that little degradation occurred during sample handling and analysis. For chemovar A, the total cannabinoid content ranged from 15.14 ± 0.50 to 16.70 ± 1.10%, with a mean of 15.50 ± 1.10% (n = 6, two samples per crop, three crops). Similarly, the cannabinoid content in chemovar B crops ranged from 16.50 ± 0.43 to 18.36 ± 0.08% with a mean of 17.60 ± 0.80% (n = 6, two samples per crop, three crops). These results agree with literature reports, which indicate average cannabinoid contents in inflorescences ranging from 5 to 25%. [Jin et al., 2021] Inspection of the results also shows that relative cannabinoid composition and total cannabinoid yield is stable through the crops in both chemovars.
|
|
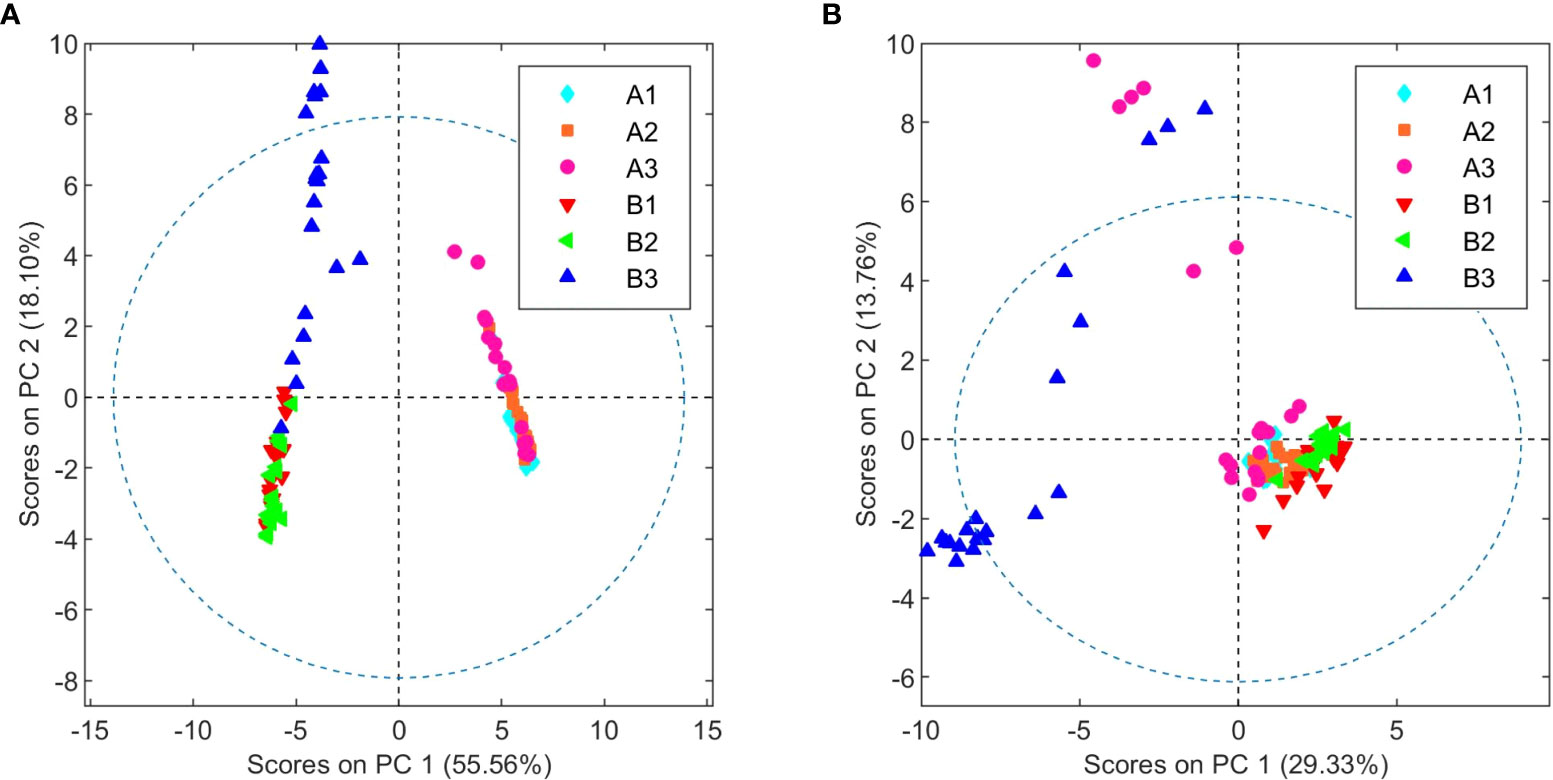
Following the determination of the basic cannabinoid composition, the metabolic profiles for both C. sativa varieties were investigated. For this purpose, 20 samples of each chemovar from the three harvests considered were collected, resulting in a total of 60 organic and 60 aqueous extract samples. PCA score plots obtained from the 1H NMR data recorded for the two sets are shown in Figure 1. It is clear that both chemovars can be easily differentiated on the basis of NMR data from their organic or aqueous extracts. Indeed, the first two principal components (PCs) account for 73.7% of the variance in the organic set, with samples from chemovar A forming a cluster showing positive PC1 scores, whereas chemovar B samples have negative scores on this PC. Similarly, only two PCs were sufficient to account for nearly 90% of the variance in the aqueous data set.
|
Cursory inspection of both PCA plots indicates that six of the aqueous samples corresponding to the third crop of chemovar A deviate from the others, suggesting errors during the preparation of these samples. On the other hand, all 20 organic and aqueous extracts from the third crop of chemovar B deviate considerably from the rest. As discussed below, this is likely associated with fungal infections affecting plants from this particular crop. Therefore, the PCA score plots were recomputed without the outliers from both chemovars. As shown in Figure 2, 1H NMR profiles from organic and aqueous extracts can still differentiate the two chemovars clearly.
References
Notes
This presentation is faithful to the original, with only a few minor changes to presentation. Some grammar and punctuation was cleaned up to improve readability. In some cases important information was missing from the references, and that information was added. The original article lists references alphabetically, but this version—by design—lists them in order of appearance.