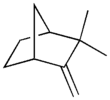
Camphene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2-Dimethyl-3-methylidenebicyclo[2.2.1]heptane | |||
| Other names
2,2-Dimethyl-3-methanylidenebicyclo[2.2.1]heptane
2,2-Dimethyl-3-methylenebicyclo[2.2.1]heptane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.123 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2319 1325 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.238 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | White or colorless solid[3] | ||
| Density | 0.842 g/cm3[3] | ||
| Melting point | 51 to 52 °C (124 to 126 °F; 324 to 325 K)[3] | ||
| Boiling point | 159 °C (318 °F; 432 K)[3] | ||
| Practically insoluble[3] | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Warning | |||
| H226, H228, H319, H410 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P273, P280, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338, P337+P313, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P501 | |||
| Flash point | 40 °C (104 °F; 313 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Camphene is a bicyclic organic compound. It is one of the most pervasive monoterpenes. As with other terpenes, it is insoluble in water, flammable, colorless, and has a pungent smell.[4] It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as turpentine, cypress oil, camphor oil, citronella oil, neroli, ginger oil, valerian, and mango.[5] It is produced industrially by isomerization of the more common alpha-pinene using a solid acid catalyst such as titanium dioxide.[6]
Camphene is used in the preparation of fragrances and as a food additive for flavoring. These include isobornyl acetate.
Biosynthesis
Camphene is biosynthesized from linalyl pyrophosphate via a sequence of carbocationic intermediates.[7]

Biosynthesis of camphene (one enantiomer) from linalyl pyrophosphate.[7]
References
- ^ IUCLID Datasheet[permanent dead link]
- ^ Fisher Scientific MSDS
- ^ a b c d e Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1736
- ^ Eggersdorfer, Manfred (2000). "Terpenes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a26_205. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Pino, Jorge A.; Mesa, Judith; Muñoz, Yamilie; Martí, M. Pilar; Marbot, Rolando (2005). "Volatile Components from Mango (Mangifera indicaL.) Cultivars". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (6): 2213–2223. doi:10.1021/jf0402633. PMID 15769159.
- ^ Sell, Charles S. (2006). "Terpenoids". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. doi:10.1002/0471238961.2005181602120504.a01.pub2. ISBN 0471238961.
- ^ a b Croteau, R.; Satterwhite, D. M.; Cane, D. E.; Chang, C. C. (1988). "Biosynthesis of Monoterpenes. Enantioselectivity in the Enzymatic Cyclization of (+)- and (-)-Linalyl Pyrophosphate to (+)- and (-)-Pinene and (+)- and (-)-Camphene". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 263 (21): 10063–71. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81477-1. PMID 3392006.
Notes
This article is a direct transclusion of the Wikipedia article and therefore may not meet the same editing standards as CannabisQAwiki.